In July 1991 at Kinokunya Books in Osaka, which had a nice selection of English-language titles, I chanced across a large paperback called Scenes of Naniwa, which seems to be subtitled, “Osaka Time Tunnel.” I’m really glad I forked over the ¥2060 to buy it (about $15 in those days), because I’ve never seen it for sale anywhere else, not even Amazon, though admittedly I only checked the English-language version of that site.
 The book has 40 short chapters, each well illustrated by black-and-white images, of Meiji- and Taisho- and early Showa-era Osaka, which is to say, the latter decades of the 19th century and the early decades of the 20th. In fact, the photographs are the genesis of the book.
The book has 40 short chapters, each well illustrated by black-and-white images, of Meiji- and Taisho- and early Showa-era Osaka, which is to say, the latter decades of the 19th century and the early decades of the 20th. In fact, the photographs are the genesis of the book.
It seems that one Teijiro Ueda (1860-1944), who owned a sizable camera shop in Osaka in the early years of the 20th century, also had a sizable collection of photographs of old Osaka. He apparently took some of them himself, though it isn’t always clear which ones. Some of them he probably collected from other photographers.
In the 1980s, with the assistance of Ueda’s elderly daughter-in-law, who had kept track of his 1,300 or so images in a dozen albums, the Yomiuri Shimbun (a daily paper) published the photos and articles to go with them in a serial format. Later the paper put the articles together in book form. A Belgian named J.V.D. Cammen took it upon himself to translate the book into English, and in 1987, Yomiuri published that too. That’s what I have.
I’m assuming that neither Japanese nor English were Cammen’s first language, and if so, he did a remarkable job. The prose isn’t quite as smooth as it might be, but on the whole it’s high-quality writing in English. Someone unfamiliar with Osaka might find the book a chore to read, but the more you know about that city, the more interesting the descriptions will be. You find yourself thinking, “That used to be there?”
It’s a time tunnel all right. The modern urban landscape of Osaka has mostly obliterated the places and sights that Scenes of Naniwa documents. (Naniwa is an older name for the city, and possibly even a poetic one in later times.) As the text notes, “In our time, with ferro-concrete buildings lining the streets, the appearance of Osaka has become almost the same everywhere, but there are plenty of photographs in the Ueda albums of the city before it received this uniformity.”
For example, the book tells of the Osaka Hotel, which used to be on Nakanoshima, a narrow island in Yoda River, which these days is a good place for strolling in fair weather. The book says that: “The hotel [had] arched windows resembling those of palaces in the West. It [had] turrets like castles in the Middle Ages, with dormer windows in the roofs, which [were] covered with asbestos slates, and the ridgepoles too [were] decorated with fine ironwork… The front part of the hotel [was] three-storied, but at the back [was] a basement with a veranda and even an anchorage for the private use of the hotel.”
The structure dated from 1900, but didn’t last long: it burned down in 1924. On the site now is the fine Museum of Oriental Ceramics, completed in 1982.
Then there’s the Tall Lantern (Taka-doro) in Sumiyoshi. I used to live in Sumiyoshi Ward, and south of my residence, about 20 minutes on foot, was Sumiyoshi Shrine (Sumiyoshi-jinja). Not far from there was the Tall Lantern, though not in its original position, as I learned from the book.
“… the Taka-doro was originally an offering made by fishermen to the Guardian Sea-god of the Sumiyoshi Shire at the end of the Kamakura period, but has become best known now for being the oldest lighthouse ever constructed in Japan… In 1950, the Stone Lantern was destroyed by Typhoon Jane, but it was reconstructed in its original form about 200 m farther east. Restored, it stands on its former foundation, is 21 m high, and has a tiled roof like that of a temple.”
Other chapters cover the Juso Ferry (Juso’s a neighborhood; I was married in a church there); the site of the Japanese Mint and its cherry blossoms; the earlier Osaka Stations, before the current and entirely utilitarian one; the site of the Industrial Expo of 1903; a ceremonial arch (long gone) built to commemorate the victory over Russia in 1905; the evolution of the Dotomburi district, which in the age of electric lights overwhelms the eye, but which used to be a home to many kabuki theaters; the earlier iterations of Namba Station and the Nankai Electric Railway; Shitennoji and environs, the clearest memory I have of which is one of the ponds at Shitennoji temple that was infested with an absurd number of frogs; and much more, such as an account of a fire on July 31, 1909, that burned more than 122 hectares of the city and 11,300 houses. Ueda apparently went to the roof of his camera store and took a picture that morning, which shows an enormous billow of black smoke about two kilometers away.
The book also taught me about the miotsukushi. I pulled this image of one, along with a sailboat, from a Japanese web site. The image is in the book, though cropped a bit differently, and dates from about 1877, which surely puts it in the public domain.
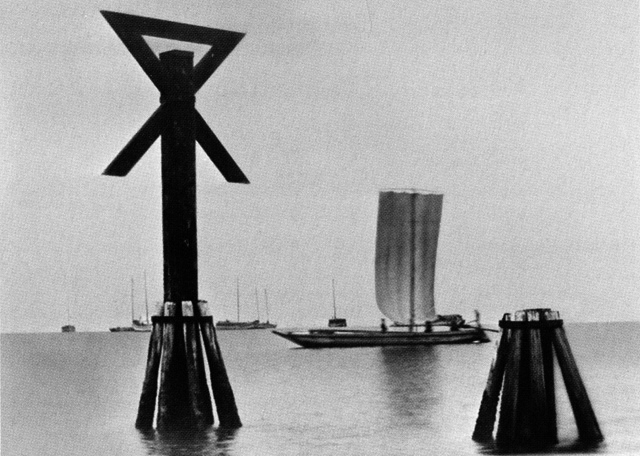 Scenes of Naniwa tells us that “the Osaka city symbol, the miotsukushi, originates from the stakes used as water route signals which up to the middle of the Meiji period stood planted in the Kizu and Aji Rivers, both debouching into Osaka Harbor. The depth of the water was difficult to judge because of the abundant bamboo reeds growing in the rivers… the miotsukushi planted along both sides of the rivers were signs showing that within those stakes the water was deep enough to sail through safely.”
Scenes of Naniwa tells us that “the Osaka city symbol, the miotsukushi, originates from the stakes used as water route signals which up to the middle of the Meiji period stood planted in the Kizu and Aji Rivers, both debouching into Osaka Harbor. The depth of the water was difficult to judge because of the abundant bamboo reeds growing in the rivers… the miotsukushi planted along both sides of the rivers were signs showing that within those stakes the water was deep enough to sail through safely.”
Though gone by the end of the 19th century, the miotsukushi were well regarded enough to become the city symbol in 1894, and if you spend enough time in Osaka, you start noticing depictions of them in various places, something like the Chicago municipal device.
Before I left Japan in 1994, I went to a flag shop and, after some discussion, managed to order a miotsukushi flag as a souvenir of my time in the city. (I think they had a hard time believing a gaijin would have ever heard of it.) It was a little bigger than a 3 x 5-inch flag, and I had it until 2003, when it disappeared during the move to my current house.